Visual representation categorises and organises ideas in a particular way. This broad term encompasses other terms such as graphic outline, structured overview and concept map. It is one of a number of pre-reading strategies which assists students to gain meaning from the text by:
- providing a context for reading which helps to activate existing knowledge of the topic
- enabling students to establish a purpose for their reading
- helping students predict what the text will be about.
Advantages of using visual representation for EAL students
- Visual representation teaches students how to recognise and use textual clues (eg heading, sub- headings, graphics). Ideally, these features support the reader of the text; particularly long, complex texts. Many students are not sure of the function of these text features and so frequently ignore them. They are thus deprived of valuable information and support.
- It helps students to recognise typical structures used in texts — the more familiar they are with the ways these texts are organised and presented, the more able they will be to read a wide range of texts independently and effectively. Exposure alone to a wide range of texts will not necessarily enable students to develop this skill of being successful readers.
- It shows students how an author has presented and organised his/her ideas and enables students to identify texts which are well organised and helps them in their own writing. It also enables students to identify texts which are not well organised and fosters a healthy critical eye.
- It enables students to make judgments about the suitability of a text for their particular reading purpose.
- It enables students to practise important skills such as:
- previewing techniques and predicting
- skimming and scanning
- note-making and summarising.
- Once students have had considerable experience in developing them, visual representation can be a useful tool for independent research and learning.
Advantages of using visual representation for teachers
Visual representation can also assist teachers in the selection of appropriate teaching/learning resources by helping them to:
- identify texts that could be useful models for student writing
- identify illogical structures, gaps in content or graphics provided and superfluous material.
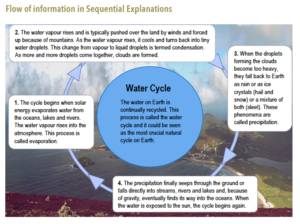
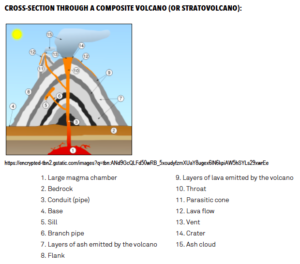
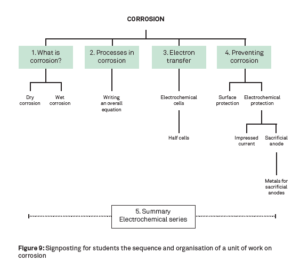
Some examples of visual representation
© John Polias, Lexis Education. This material may not be reproduced or distributed, in whole or in part, without the prior written permission of Lexis Education.
Do you want to be notified of new posts by email? Subscribe to our newsletter here.